FAQs about myasthenia gravis treatment
The best treatment for myasthenia gravis will vary depending on a person’s symptoms and their severity, the cause and type of the disease, and other health factors. Treatment regimens may change over time as a person’s disease evolves. Patients should work with their individual healthcare teams to decide on an appropriate course of treatment in their particular case.
Whether myasthenia gravis treatments are covered by a person’s insurance — and to what degree they’re covered — will depend on each person’s particular insurer and plan. Patients are advised to speak with their healthcare team and insurance company when starting a new treatment to understand their individual coverage. Some companies marketing myasthenia gravis medications also offer support in navigating the insurance process and accessing financial assistance programs.
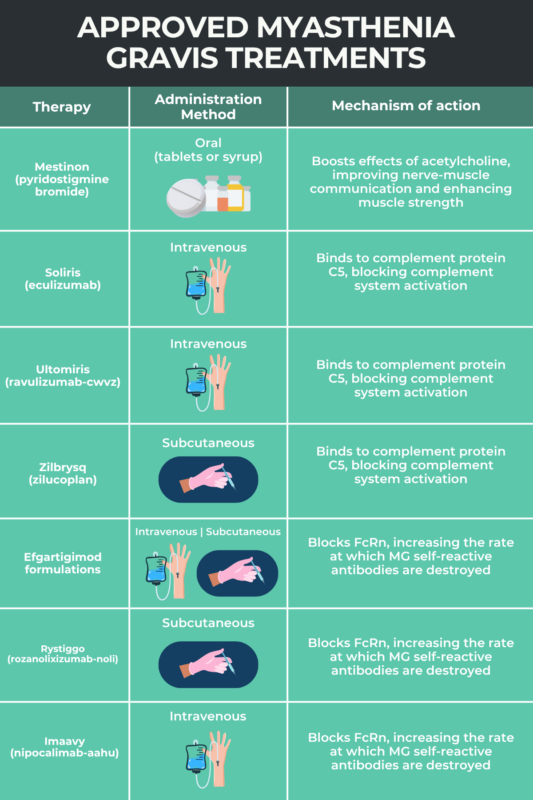
There is no cure for myasthenia gravis, but there are several treatments, including medications, plasmapheresis (plasma exchange), and surgery, that can help ease its symptoms. Many of these treatments work to either suppress the activity of the immune system or improve nerve-muscle communication to alleviate symptoms of muscle weakness and fatigue.
Although they work through different mechanisms, myasthenia gravis treatments are intended to ease or prevent the symptoms of muscle weakness and fatigue that characterize the neuromuscular disease. These treatments usually do so by either suppressing the immune system or enhancing nerve-muscle communication.
A number of medications exist that can help manage myasthenia gravis symptoms. Medications for myasthenia gravis, or MG for short, can be divided into multiple groups depending on their mechanism of action, to include anticholinesterases, complement system inhibitors, FcRn blockers, corticosteroids, or non-steroidal immunosuppressants. However, none of these therapies provides a definite cure for the condition.
 Fact-checked by
Fact-checked by